Lion's mane: a mushroom that shows promise for the brain
Lion's mane, or hedgehog mushroom (Hericium erinaceus), is a mushroom being studied by scientists for its potential effects on the brain, cognitive functions and the nervous system.
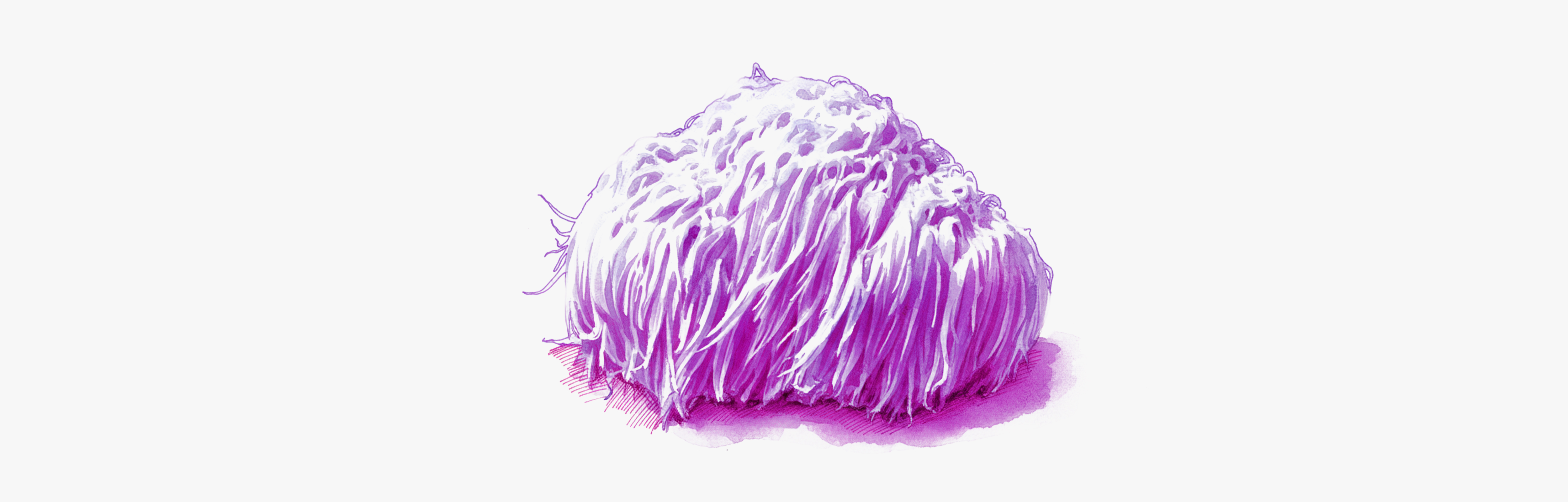

Hericium erinaceous: the hedgehog with the evocative name
Lion's mane owes its name to its unusual appearance: a white mass of long, hanging prickles resembling a wild mane.
This mushroom belongs to the Hericiaceae family and grows naturally on decaying tree trunks, mainly in East Asia, North America and Europe.
It has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine, where it is reputed to have anti-infection and nerve-boosting properties (1).
These traditions provide an interesting basis for modern research, which is exploring the possible effects of this mushroom on the brain and nervous system.
The potential benefits of lion's mane for the brain
Studies suggest that lion's mane may have positive effects on memory, concentration and neuroplasticity (2). However, it is important to note that these observations remain preliminary for the time being, based mainly on in vitro studies, animal studies or small clinical trials.
1. Potential support for memory and concentration
Research indicates that certain compounds extracted from lion's mane may help to improve cognitive performance and mood.
These effects are thought to be linked to a stimulation of neurogenesis, i.e. the formation of new neurons, as well as an improvement in synaptic functions, which are essential for the transmission of information between nerve cells (3).
2. Possible action on cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders
In addition to its effects on memory, some experimental data suggest that lion's mane may have a protective role against neurodegenerative disorders. The mushroom appears to be able to act on several key mechanisms involved in neuronal degeneration.
A recent study showed that certain extracts of Hericium erinaceus could help limit oxidative stress and inflammation in brain cells (4), two factors known to promote cognitive decline.
Finally, a small study of patients with mild cognitive impairment showed a temporary improvement in cognitive function, which suggests that further research is needed into neurodegenerative diseases, including ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis).
For those wishing to explore the possible benefits of lion's mane, several food supplements based on this mushroom are now available.
It's worth noting that powdered Hericium has a subtle, light taste, similar to that of seafood, particularly lobster or scallops. So don't be surprised!
![]() Discover the Lion's Mane supplement, formulated to support nervous functions and cerebral well-being.
Discover the Lion's Mane supplement, formulated to support nervous functions and cerebral well-being.
The action of lion's mane on neurogenesis and neuroprotection
The beneficial potential of lion's mane for the cognitive sphere is based on several bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, hericenones and erinacins.
These molecules are at the heart of current research into how this mushroom might influence the brain.
Nerve growth factor (NGF): the driving force behind neurogenesis
A major discovery is lion's mane's supposed ability to stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF).
NGF is a protein that is thought to promote the survival, growth and differentiation of neurons, particularly in the hippocampus, a key region for memory and learning.
A study published in Biomedical Research in 2008 (5) showed that extracts of Hericium erinaceus could induce NGF synthesis in cell cultures, suggesting a neurotrophic effect.
This stimulation of NGF could partly explain the observations of improved cognitive capacity in treated subjects.
Polysaccharides and neuroprotective effects
The polysaccharides contained in lion's mane are also thought to play an important role.
The study by He et al. (2017) (6) describes the polysaccharides present in lion's mane, detailing their chemical composition and their various actions observed at the cellular level.
These compounds appear to play a role in modulating oxidative stress and inflammation, two processes often linked to brain ageing. They could also influence the immune system.
A possible effect on blood sugar regulation
Lion's mane could also play a role in regulating metabolism.
A recent study identified several compounds present in the mushroom, including erinacenols A to D, capable of inhibiting the activity of the enzyme α-glucosidase (7).
This enzyme is thought to be involved in the digestion of carbohydrates and the regulation of blood sugar levels. These results suggest a potential beneficial effect in the treatment of diabetes and metabolic disorders, to be confirmed by in vivo research.
To date, more than 70 bioactive compounds have been identified, but further research is essential to better understand their potential against chronic and neurological diseases.
Among these compounds, the action on nerve growth factor appears to be one of the greatest potential benefits of lion's mane. The mushroom is also thought to have an interesting function in cases of anxiety and depression (8).
Good to know: It is better to consume lion's mane at the start of the day to optimise its effects on the nervous system and its adaptogenic properties.
SUPERSMART ADVICE
References
- Muhanna M, Lund I, Bromberg M, Wicks P, Benatar M, Barnes B, Pierce K, Ratner D, Brown A, Bertorini T, Barkhaus P, Carter G, Mascias Cadavid J, McDermott C, Glass JD, Pattee G, Armon C, Bedlack R, Li X. ALSUntangled #73: Lion's Mane. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 2024 May;25(3-4):420-423. doi: 10.1080/21678421.2023.2296557. Epub 2023 Dec 23. PMID: 38141002.
- Szućko-Kociuba I, Trzeciak-Ryczek A, Kupnicka P, Chlubek D. Neurotrophic and Neuroprotective Effects of Hericium erinaceus. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 3;24(21):15960. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115960. PMID: 37958943; PMCID: PMC10650066.
- He X, Wang X, Fang J, Chang Y, Ning N, Guo H, Huang L, Huang X, Zhao Z. Structures, biological activities, and industrial applications of the polysaccharides from Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane) mushroom: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Apr;97:228-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.040. Epub 2017 Jan 10. PMID: 28087447.
- Kushairi N, Phan CW, Sabaratnam V, David P, Naidu M. Lion's Mane Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. Suppresses H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage and LPS-Induced Inflammation in HT22 Hippocampal Neurons and BV2 Microglia. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 1;8(8):261. doi: 10.3390/antiox8080261. PMID: 31374912; PMCID: PMC6720269.
- Hericenones and erinacines: stimulators of nerve growth factor (NGF) biosynthesis in Hericium erinaceus. Publié dans Biomedical Research (Tokyo), 2008, volume 29, numéro 4, pages 231-237. DOI : 10.2220/biomedres.29.231
- He X, Wang X, Fang J, Chang Y, Ning N, Guo H, Huang L, Huang X, Zhao Z. Structures, biological activities, and industrial applications of the polysaccharides from Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane) mushroom: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Apr;97:228-237. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.040. Epub 2017 Jan 10. PMID: 28087447.
- Lee SK, Ryu SH, Turk A, Yeon SW, Jo YH, Han YK, Hwang BY, Lee KY, Lee MK. Characterization of α-glucosidase inhibitory constituents of the fruiting body of lion's mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus). J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Nov 15;262:113197. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113197. Epub 2020 Jul 29. PMID: 32738392.
- Friedman M. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health-Promoting Properties of Hericium erinaceus (Lion's Mane) Mushroom Fruiting Bodies and Mycelia and Their Bioactive Compounds. J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Aug 19;63(32):7108-23. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02914. Epub 2015 Aug 5. PMID: 26244378.
Keywords
2 Days
very good expereince
very good expereince
Jelena Đaković
2 Days
Very good products.
Very good products.
Agnes BENDSAK
4 Days
Just OK
Just OK, ordering from company for many years and being safisfied
Lynn Mae
5 Days
Recomendo
Produtos encomendados são recebidos atempadamente e de acordo com o anunciado! Muito satisfeita!
Carla Sofia
5 Days
Everything is great!
Everything is great!
Jonas
10 Days
The delivery was fast and the product…
The delivery was fast and the product is great
SOMMARIVA Gianni
11 Days
Great service and lots of information
Great service and lots of information
Gabi
14 Days
Service Satisfaction
I’m satisfied with the service; it fulfilled what it set out to do.
Anfhony Abreu
17 Days
Original product and fast delivery
Original product and fast delivery. I haven't started it yet, but will do soon.
Vincenza Catania
20 Days
Good quality
Good quality. Good service.
Leonel Guzman
22 Days
Top!!!!!!!!
Top!!!!!!!!
Michael
24 Days
Excellent!
Products are great and delivered fast!
PARDINI Debora
25 Days
From order to receive the product
From order to receive the product, the process is smooth & fast. It’s good to customers.
WONG Mei Ling
26 Days
Fast delivery
very quick delivery to italy. product is good.
Customer
27 Days
Prompt delivry !!👍
Prompt delivry !!👍
SWEET Christine
of experience
your money back
##montant## purchase